We all witnessed the changes after 2014, when our honourable Prime Minister became this nation’s prime representatives.
His government changes the names of roads, removing Mugal rulers history and adding on our own country’s brave soldiers.
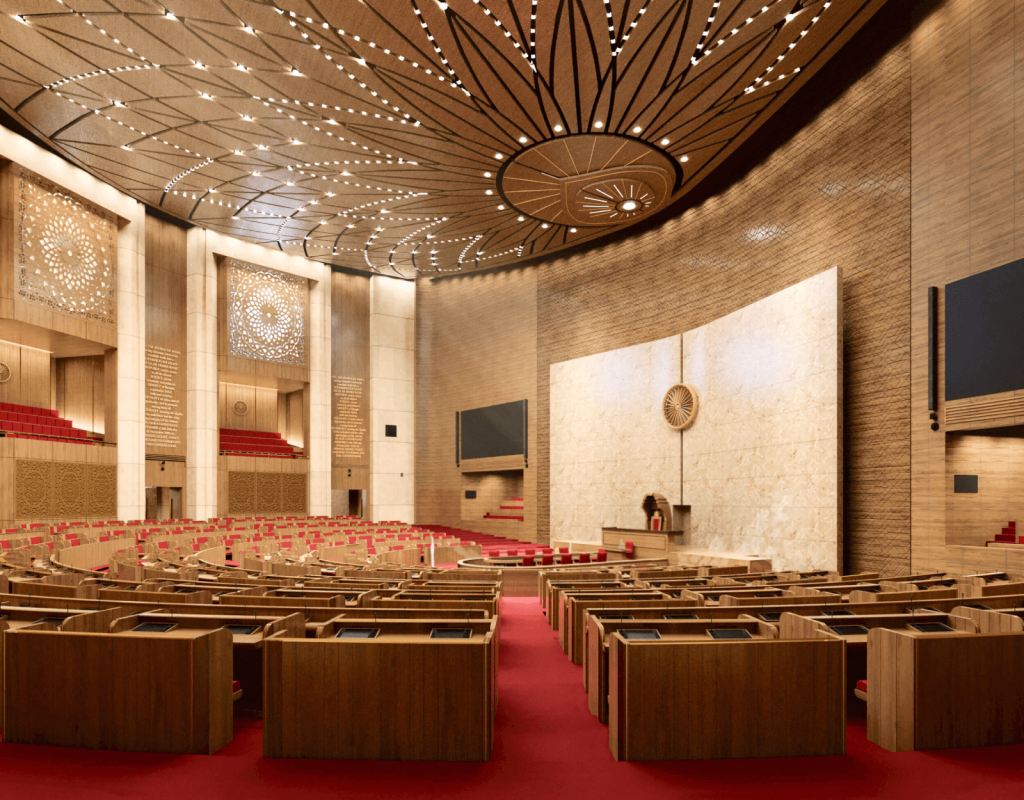
Like these changes, the PM is also changing the old parliament to the new one, with upgraded technical systems and space, which will impact our International relations as well.
What is Parliament of India?

The country’s top legislative body is the Indian Parliament. It is a bicameral institution, having two houses: the Lok Sabha (House of the People) and the Rajya Sabha (Council of States).
i)Rajya Sabha: The Rajya Sabha is the Parliament’s upper house. It stands in for India’s states and union territories. According to the proportional representation system, members of State Legislative Assemblies elect the Rajya Sabha.
ii)Lok Sabha: The Lok Sabha is the Parliament’s lower house. It stands in for the Indian populace. Through general elections, eligible Indian voters elect members of the Lok Sabha directly.
History of Parliament of India
After India was freed from British colonial rule, the Indian Parliament was established.
Several years were spent on the Constitution’s drafting, and the makeup of the Parliament were discussed, debated, and deliberated.
The final draught of the Constitution was approved by the Constituent Assembly on November 26, 1949.
It became operative on January 26, 1950.
As a result, by passing the Indian Constitution, the Constituent Assembly created the Indian Parliament.
Importance of Parliament of India
- Legislative Roles: The Parliament’s main responsibility is to pass laws. Legislation addressing a wide range of topics, such as governance, social welfare, economic policies, and more. Members of Parliament (MPs) introduce and discuss this.
- Representation:The people choose MP’s to represent them in the legislative process. They represent their constituents’ interests and voice their worries, making sure that different facets of society are heard and taken into account.
- Oversight : The Parliament has oversight authority over the President, Prime Minister, Council of Ministers, and various government agencies, as well as the executive branch of the government as a whole. MPs have the power to grill ministers, examine government programmes and initiatives, and hold the executive branch responsible for its choices. This promotes good governance, accountability, and transparency.
- Budget Approval: In the budgetary process, the Parliament is essential. The annual budget that the government submits is up for discussion and approval in Parliament. The MP’s examine,discuss and also give suggestions of budget by voting.
- Amendments to the Constitution: The Indian Parliament has the authority to change the constitution. It takes a two-thirds majority in both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha to approve a constitutional amendment. Through this process, the Constitution can change and improve to meet changing circumstances and societal demands.
- Forum for Debate and Discussion: The Parliament acts as a stage for public discussions and debates on domestic issues. It gives MPs a platform to voice their opinions, have frank discussions, and look for solutions to the nation’s most pressing issues.
- Symbol of Democracy: The Parliament of India represents the functioning democracy in India. It embodies the principles of inclusivity, diversity, and democratic governance. It ensures that decisions are made using democratic procedures and represents the people’s collective will and aspirations.
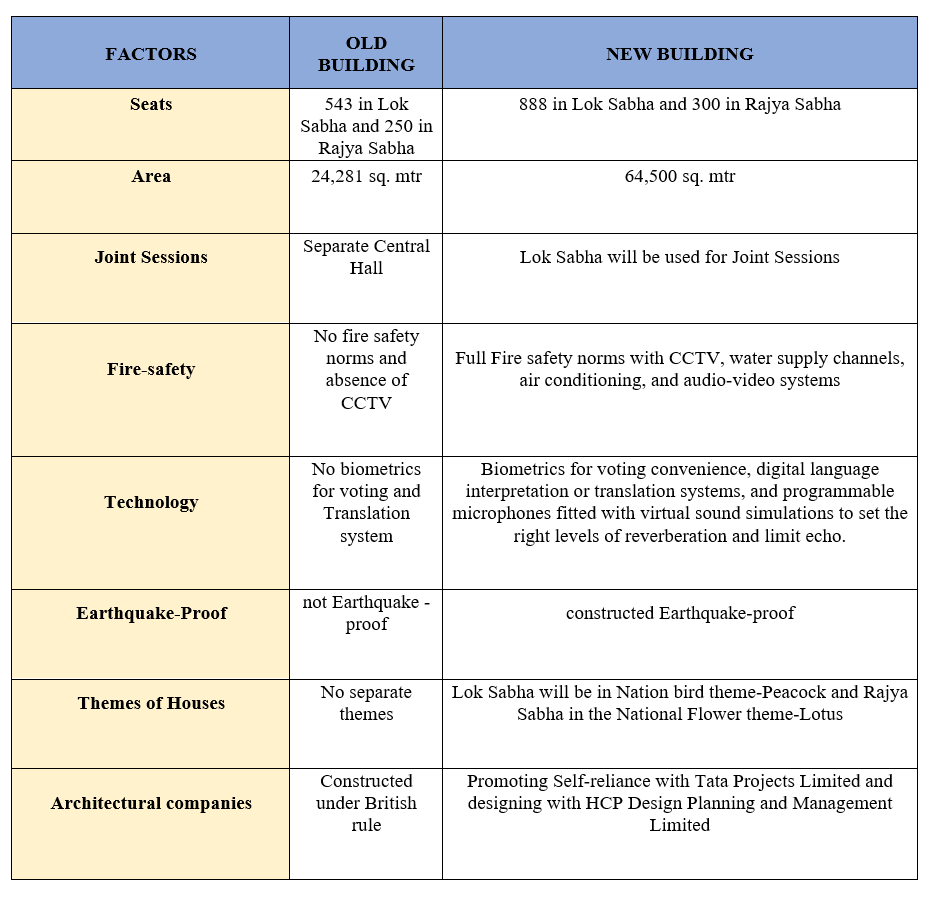
Major Differences between Old and New Parliament Building